THE DIFFERENT CAST IRON / MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS: from lamellar graphite cast iron (FGL/Grey Iron) to spheroidal graphite cast iron (FGS)
Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon. We differentiate between two large families, lamellar graphite cast iron (FGL), also known as "grey cast iron", and spheroidal graphite cast iron (FGS).
Cast iron is often compared to steel, but what is the difference?
Steel has a carbon content of less than 2%, whereas cast iron has a carbon content of more than 2%.
To obtain each type of cast iron, we can add a chemical element that will modify its structure and have an impact on the mechanical characteristics.
These are called "alloyed cast irons".
- Silicon (Si) / graphitising element : increases elongation, favours the precipitation of graphite, thus the creation of ferrite and prevents the formation of carbide.
- Nickel (Ni) / graphitising element : increases shock and corrosion resistance, balances the structure between the thin and thick parts
- Copper (Cu) : increases mechanical properties, increases hardness and refines the pearlite.
- Manganese (Mn) : increases mechanical properties, increases hardness and provides carbides.
Flake or spheroidal graphite? What are the differences?
The flake graphite cast iron (FGL) family:
The graphite is found in the form of flakes. It is this lamellar form of graphite (notch effect) that makes GL cast irons brittle. On the other hand, the graphite improves the friction characteristics of the cast iron and therefore facilitates machining.
The advantages :
- Good machinability
- Stiffness
- Resistance to corrosion and compression
- Good vibration absorption
- Excellent castability
The less :
- Fragile compared to steels and GS cast iron
Grey cast iron can be studied using the stable iron-graphite diagram. However, the following conditions must be met: having a graphitising element (see list above), having a slow cooling and a high casting temperature. Note that as the temperature drops, the graphitising factors no longer have an effect, so the diagram will be metastable.
The types of FGL :
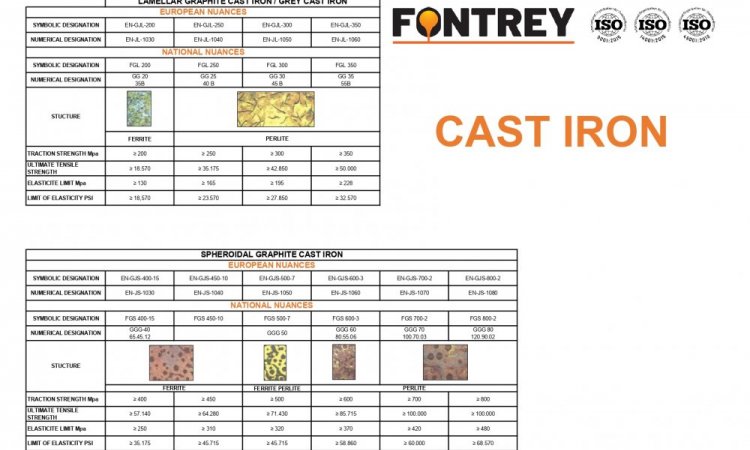
- EN-GJL-200 / EN-JL-1030 / FGL 200 / GG20 / 35B
Structure: Ferrite
Tensile strength Mpa: ≥ 200
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 18.570
Yield strength: ≥ 130 Mpa or ≥ 18.570 PSI
- EN-GJL-250 / EN-JL-1040 / FGL 250 / GG25 / 40B
Structure: Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa: ≥ 250
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 35.715
Yield strength: ≥ 165 Mpa or ≥ 23.570 PSI
- EN-GJL-300 / EN-JL-1050 / FGL 300 / GG25 / 45B
Structure: Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa: ≥ 300
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 42.850
Yield strength: ≥ 195 Mpa or ≥ 27.850 PSI
- EN-GJL-350 / EN-JL-1060 / FGL 350 / GG35 / 55B
Structure: Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa: ≥ 350
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 50.000
Yield strength: ≥ 228 Mpa or ≥ 32,570 PSI
The spheroidal graphite cast iron (SGG) family:
The graphite is found in the form of nodules (spheroids). This particular microstructure is obtained by adding magnesium to the cast iron, shortly before casting, this is the spheroidisation treatment. The magnesium evaporates but causes rapid crystallisation of the graphite in the form of nodules. This microstructure gives it mechanical characteristics similar to steel. Indeed, the spheroidal shape of the graphite gives the cast iron a good ductility
The advantages :
- High mechanical characteristics
- High ductility
- Good machinability in ferritic structure and fairly good in perilitic structure
- Good castability and weldability
- Good elasticity
Types of FGS :
- EN-GJS-400-15 / EN-JS-1030 / FGS 400-15 / GGG 40 / 65.45.12
Structure: Ferrite
Tensile strength Mpa : ≥ 400
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 57.140
Yield strength: ≥ 250 Mpa or ≥ 35.715 PSI
Elongation: ≥ 15%
- EN-GJS-450-10 / EN-JS-1040 / FGS 450-10
Structure: Ferrite
Tensile strength Mpa: ≥ 450
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 64.280
Yield strength: ≥ 310 Mpa or ≥ 44.286 PSI
Elongation: ≥ 10%
- EN-GJS-500-7 / EN-JS-1050 / FGS 500-7 / GGG 50
Structure: Ferrite/Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa: ≥ 500
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 71.430
Yield strength: ≥ 320 Mpa or ≥ 45.715 PSI
Elongation: ≥ 7%
- EN-GJS-600-3 / EN-JS-1060 / FGS 600-3 / GGG 60 / 80.55.06
Structure: Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa : ≥ 600
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 85.175
Yield strength: ≥ 370 Mpa or ≥ 52.860 PSI
Elongation: ≥ 3%
- EN-GJS-700-2 / EN-JS-1070 / FGS 700-2 / GGG 70 / 100.70.03
Structure: Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa : ≥ 700
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 100.000
Yield strength: ≥ 420 Mpa or ≥ 60.000 PSI
Elongation: ≥ 2%
- EN-GJS-800-2 / EN-JS-1080 / FGS 800-2 / GGG 80 / 120.90.02
Structure: Perlite
Tensile strength Mpa : ≥ 800
Ultimate tensile strength: ≥ 114.285
Yield strength: ≥ 480 Mpa or ≥ 68.570 PSI
Elongation: ≥ 2%
At FONTREY, we offer all of these cast irons for use in various industries.
Below, find our summary table of the different cast irons.
Do you have a question? Please contact us !